

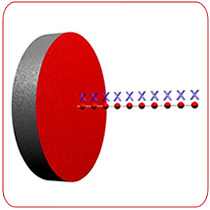
Putting together Faraday’s equation (magnitude) and Lenz’s equation (polarity), we get the following:Īlternate Naming Conventions-Faraday-Lenz Law and Moreīecause Faraday’s law, Lenz’s Law, and Maxwell’s equations are so closely related to each other, you may see other names used for these laws including: When the north pole of the magnet in the figure above moves closer to or further from the loop, an EMF will be created with polarity such that the induced current in the loop will create a magnetic field that opposes the changing magnetic field from the magnet. Faraday’s law and Lenz’s law define the induced EMF generated in a coil by a changing magnetic field To put it simply, the induced current opposes the changing magnetic flux which is producing it, as shown in Figure 1.įigure 1. To determine the polarity of the induced EMF, we must turn to Lenz’s law which states that when a changing magnetic field induces a current in a conducting coil, the induced current will generate a magnetic field that opposes the inducing magnetic field. $$dt$$ = the time over which the change in flux occurred, in seconds.$$d\theta$$ = the change in magnetic flux, in webers.N = the number of turns in a coil of wire.$$\epsilon$$ = the electromotive force, in volts.Faraday’s equation only tells us the magnitude of the EMF, not the polarity: This EMF, measured in volts, will also create a current flow. You can enter any three of the four variables:įrom there, the calculator will return the result for the fourth variable.įaraday’s law of electromagnetic induction states that any change in a magnetic field will induce an electromotive force in a conductive coil that is directly proportional to the rate of change in the inducing magnetic field. Network Difficulty and Hashrate Explained.The application of this calculator is when trying to understand the force and voltage generated by a changing magnetic field around a closed loop. Network hashrate is calculated using the current network difficulty, the average block find time set by the cryptocurrency network and/or the effective block find time of the latest blocks. Currently, Flux (ZelCash) network hashrate is 6.17 MS/s = 6 167 144 S/s. What Is Mining? What is network hashrate? How is it calculated? Flux (ZelCash) network hashrate reflects the overall performance of all miners in the flux network. Once it is found, the problem is changed, and miners all over the world start searching for another solution. Miners are solving the hash function and searching for a potential block solution until they find the right one. This is what one solution of a hash function, or a hash, means.

Miners solve a hash function set by a cryptocurrency algorithm multiple times in a second.
FLUX CALCULATOR SOFTWARE
A solution is a result gained after one cycle of mining software operation. In other words, it is solving a sol function 40.1 times per second. It means that it is calculating solutions per second. For example, one Nvidia 1070 Ti graphics card has a hashrate of 40.1 S/s, according to the 2CryptoCalc mining profitability calculator. Your GPU or mining rig is calculating thousands, millions of sol (solutions) per second. Mining performance is measured in S/s (sol per second). A solution in the Flux (ZelCash) network is called a sol, or simply S.
What is hashrate? How is it measured? Hashrate reflects the performance of mining hardware.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
